Pulmonary Function Test
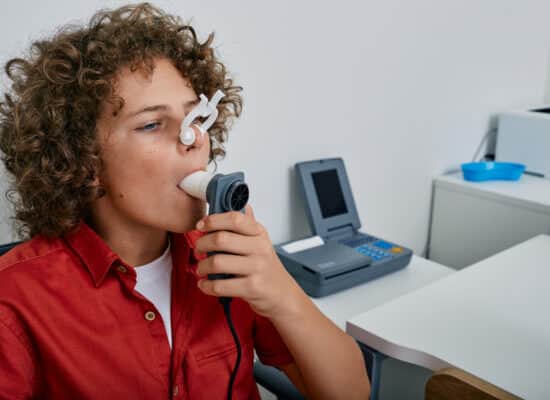


Pulmonary Function Tests (PFT) are a series of non-invasive tests to learn how well your lungs are working. The results show how well you move air in and out of your lungs and how well oxygen enters your blood stream.
What do PFTs measure?
- Vital Capacity (VC) – Total volume of air exhaled after inhaling as much as you can.
- Functional residual capacity (FRC) – Amount of air left in lungs after exhaling normally.
- Residual volume (RV) – Amount of air left in the lungs after exhaling as much as you can.
- Total lung capacity (TLC) – Total volume of the lungs after inhaling as deeply as possible.
- Forced vital capacity (FVC) – Amount of air exhaled forcefully and quickly after inhaling as deeply
as possible. - Forced expiratory volume (FEV) – Amount of air exhaled after during the first, second, and third
seconds of the FVC maneuver. - Forced expiratory flow (FEF) – Average rate of flow during the middle half of the FVC maneuver.
- Peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR) – The fastest rate that air is forced out of the lungs.
- Thoracic gas volume (TGV) – Absolute volume of gas contained in the chest when the airway is
occluded during plethysmography. - Airway resistance (Raw) – Degree of resistance to air flow when inhaling and exhaling.
Why are Pulmonary Function Tests Done?
- Diagnose lung disease (e.g. asthma, bronchitis, and emphysema).
- Determine severity of disease.
- Measure progress of chronic lung problems.
- Assess the effectiveness of treatment for chronic lung conditions.
- Determine if occupational exposure to contaminants has affected lung function.
- Identify changes in your lungs’ ability to transfer oxygen to your blood.
- Check lung function before surgery or other procedures in patients who have health conditions or
are smokers.
How to Prepare for Pulmonary Function Tests
- Be sure to tell your physician if you take any medications, as you may be instructed to stop taking certain medications before the test.
- Avoid taking any bronchodilator medications 4 hours prior to testing.
- Do not consume caffeine 3-4 hours prior to testing.
- No smoking within one hour of testing.
- Do not eat a heavy meal within one hour of testing.
- Avoid strenuous exercise at least 30 minutes prior to testing.
What Should You Expect During Pulmonary Function Testing?
- A full PFT on average will last 30 – 60 minutes.
- You will be sitting and a soft nose clip will be placed to ensure all your breathing is through your mouth and no air enters or exits the nose during the test.
- You will form a tight seal with your mouth over a sterile mouthpiece that is attached to a device that
measures the airflow and volume within the lungs. - You will be instructed to inhale and exhale in different ways. It is important that you are able to follow
clear and simple directions. - The test requires forced breathing which may cause temporary shortness of breath, light headedness,
or fatigue. - Short-acting bronchodilator medications are commonly administered to assess your lungs response and determine if this medicine could be helpful to use.
- All tests will be repeated a minimum of 2 – 3 times.

